Analyzing the Fiscal Impact of the Energy Deregulation Constitutional Amendment
A proposed 2020 ballot initiative currently making its way through the process, if approved by 60 percent or more of the voters, would deregulate only the segment of Florida’s energy market served by the investor-owned utilities (IOUs). Under the proposed language, IOUs would be limited to the construction, operation, and repair of electrical transmission and distribution systems, while municipal and cooperative utilities would have discretion whether to opt into competitive markets. The Florida Legislature would be required to create laws and regulations providing for competitive wholesale and retail markets for electricity generation and supply, and consumer protections, by June 1, 2023 and fully implement the new system by June 1, 2025.
There are a variety of significant tax and revenue implications of this amendment, and this Florida TaxWatch analysis finds that, unless very significant increases in the price of electricity for Floridians result, adoption of the proposed constitutional amendment will have a negative impact on state and local government revenues. These impacts have the potential to be relatively large. Of course, the Legislature and local governments can change the tax structure in an attempt to offset any revenue loss, but that road is fraught with peril.
This analysis provides estimates for both 2018 and 2026. The impacts were first estimated for 2018, the year of the latest tax data. Those estimates were then projected out to 2026—the expected first full year of implementation if the amendment were to pass.
The estimates are as follows:
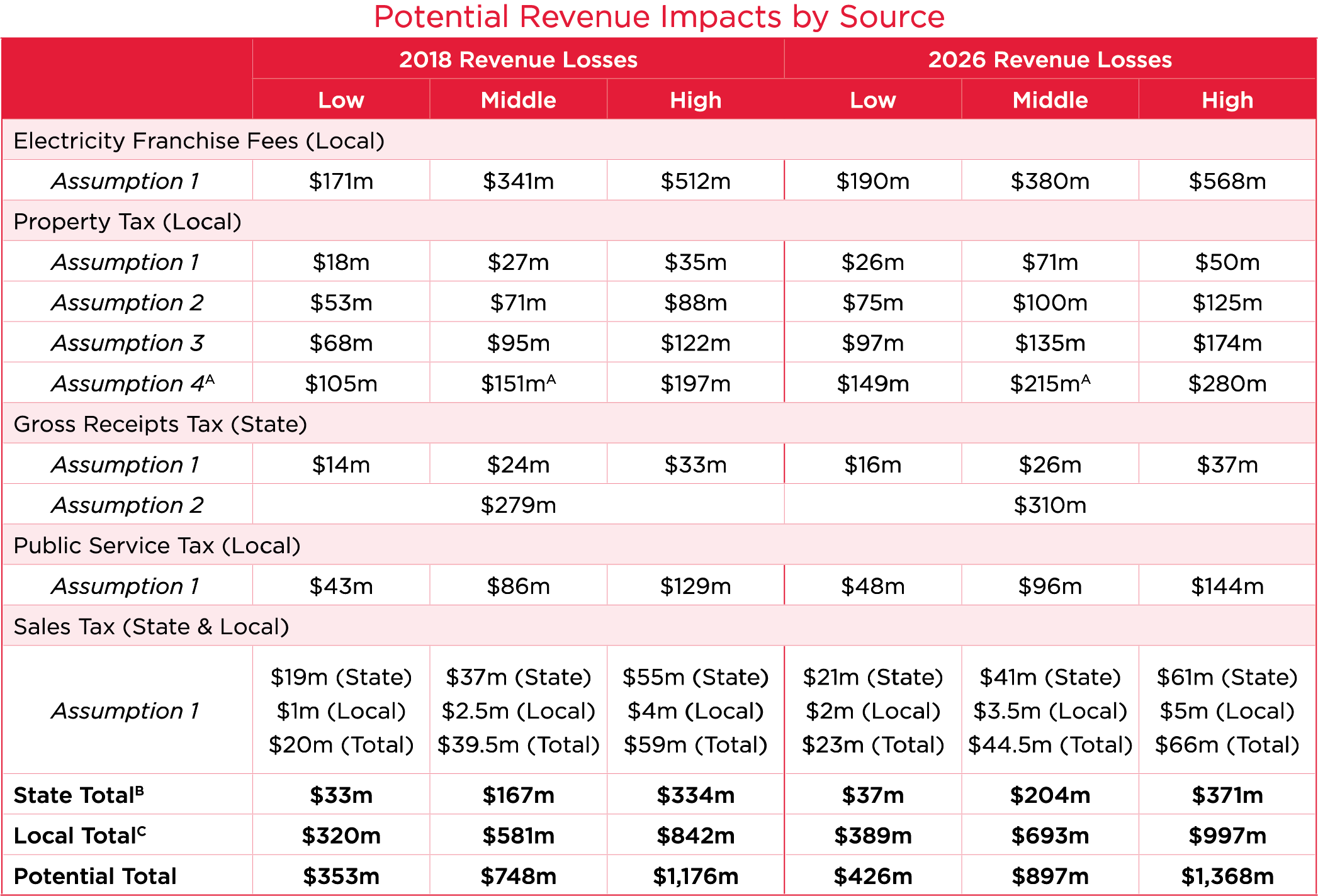
A Assumption 4 is a combination of the previous assumptions plus a loss of value from non-generation property, therefore the mid-point of assumption 4 represents the mid-point of the combination of the assumptions.
B State total includes the Gross Receipts Tax and State Sales Tax
C Local total includes the Franchise Fees, Property Taxes, Public Service Tax, and Local Sales Tax
Note: local estimates do not include any revenue from the state 6% sales tax (local government half-cent sales tax, county and municipal revenue sharing, and fiscally constrained counties).